Specially scaffolded DELs
With a new strategy of displaying chemical diversity elements on a defined macrocyclic scaffold, we attempted to mimic an antibody–antigen-like
recognition [1]. Encoding of the displayed combinations was achieved using adaptor-mediated ligation of distinctive DNA tags, and three diversity elements were introduced by split-and-pool synthesis onto orthogonally accessible lysine residues of the macrocycle projecting to the same plane of the macrocycle (see Figure). This strategy resulted in a DEL with a library size of 35,393,112 compounds.
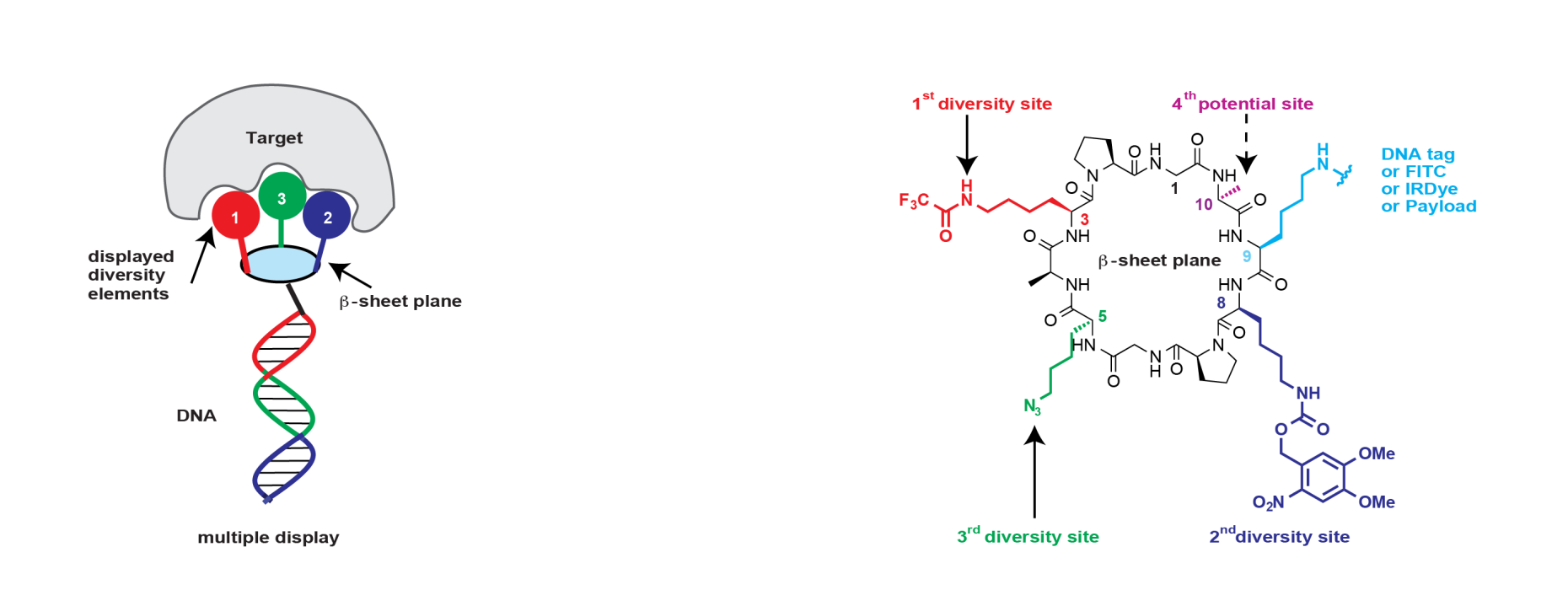
Specific binders could be isolated against a variety of proteins, including carbonic anhydrase IX, horseradish peroxidase, tankyrase 1, human serum albumin, alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, calmodulin, prostate-specific antigen and tumour necrosis factor. Similar to antibodies, the encoded display of multiple chemical elements on a constant scaffold enabled practical applications, such as fluorescence microscopy procedures or the selective in vivo delivery of payloads to tumors.
Furthermore, photo-crosslinking facilitated the generation of protein-specific chemical probes [1].
[1] Li, Y., De Luca, R., Cazzamalli, S., Pretto, F., Bajic, D., Scheuermann, J.* & Neri, D.* (2018), Nat Chem. 10, 441-448.
external page https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0017-8